Network Note
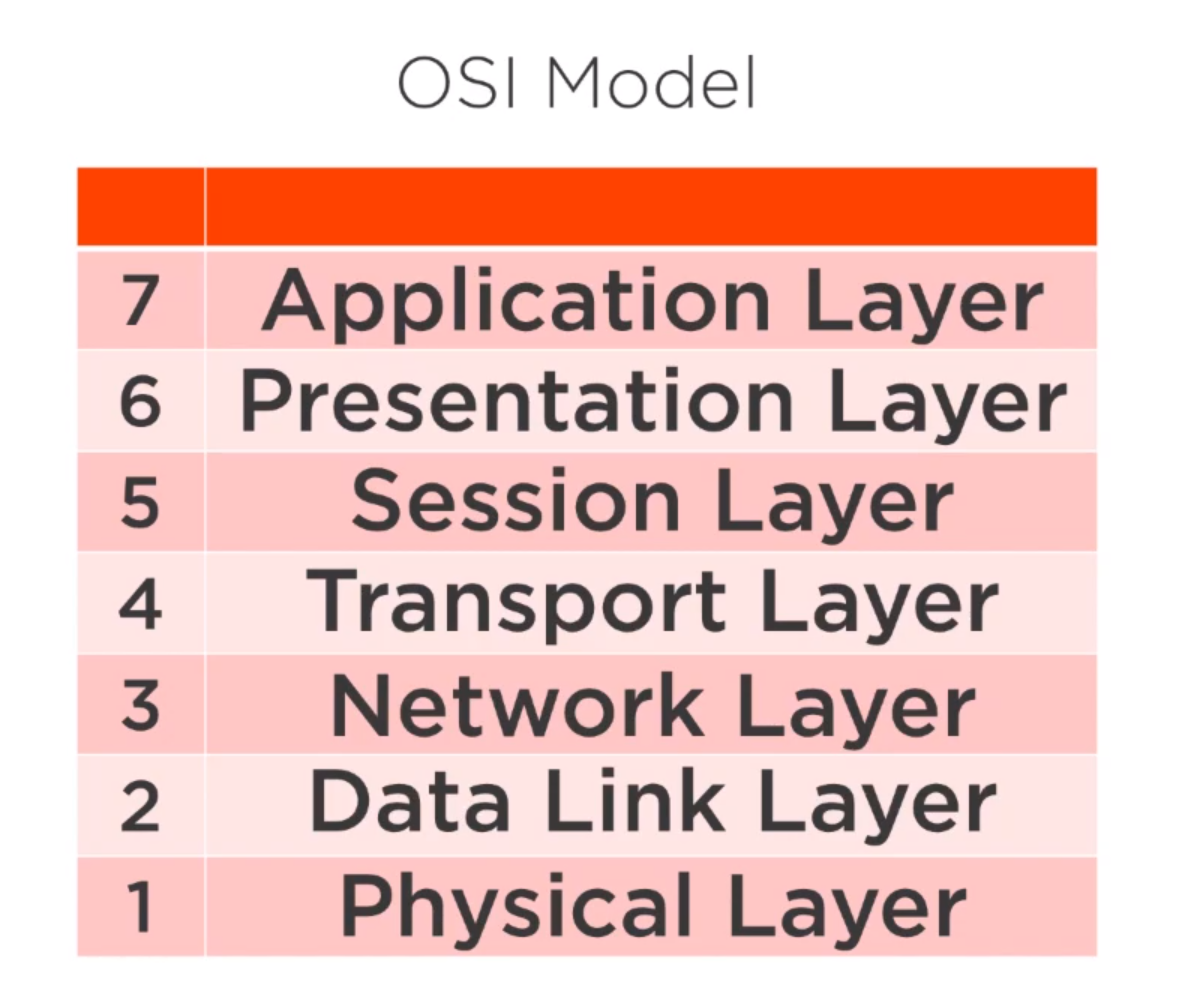
OSI Model
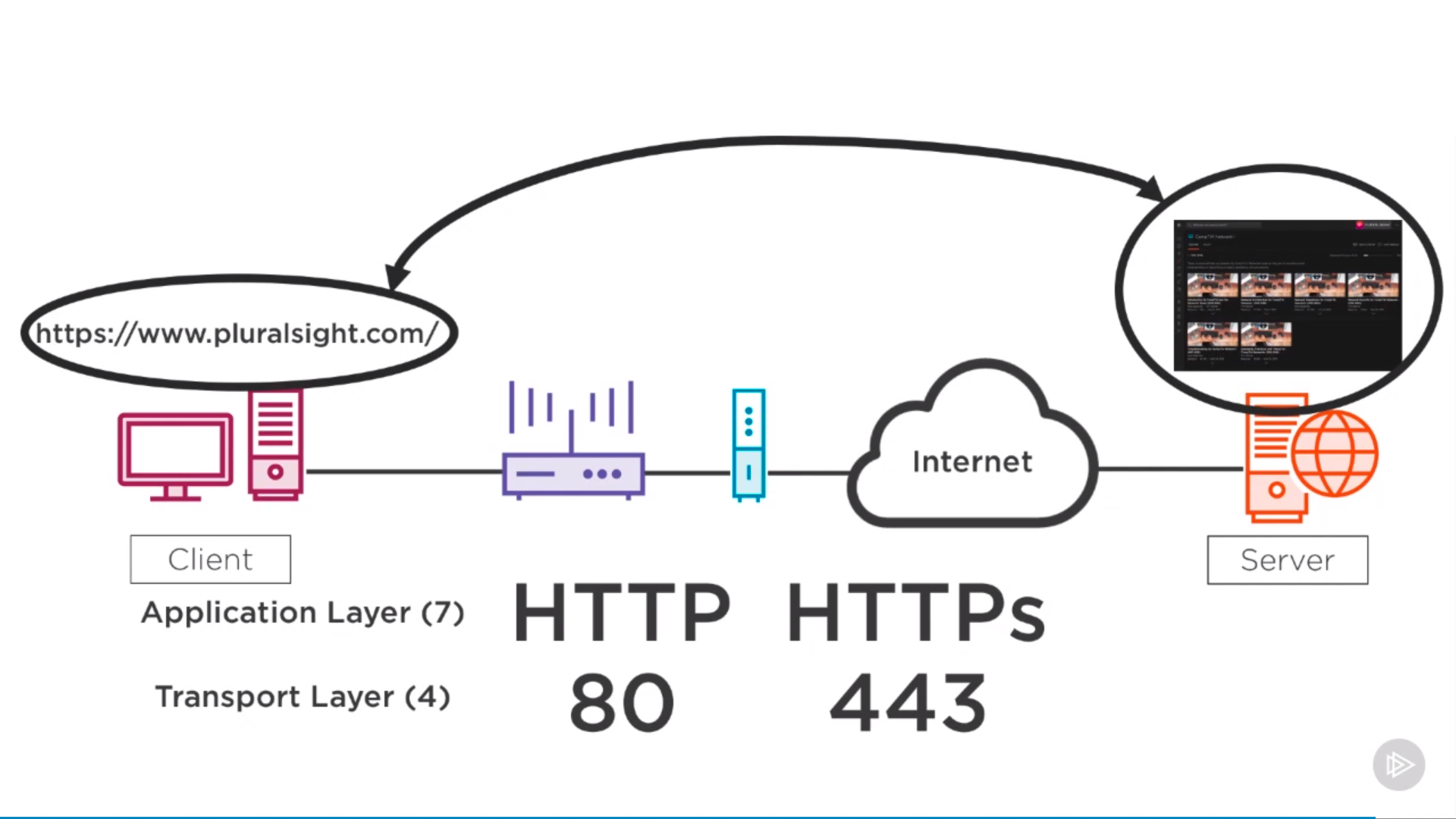
Protocols
Data Transfer
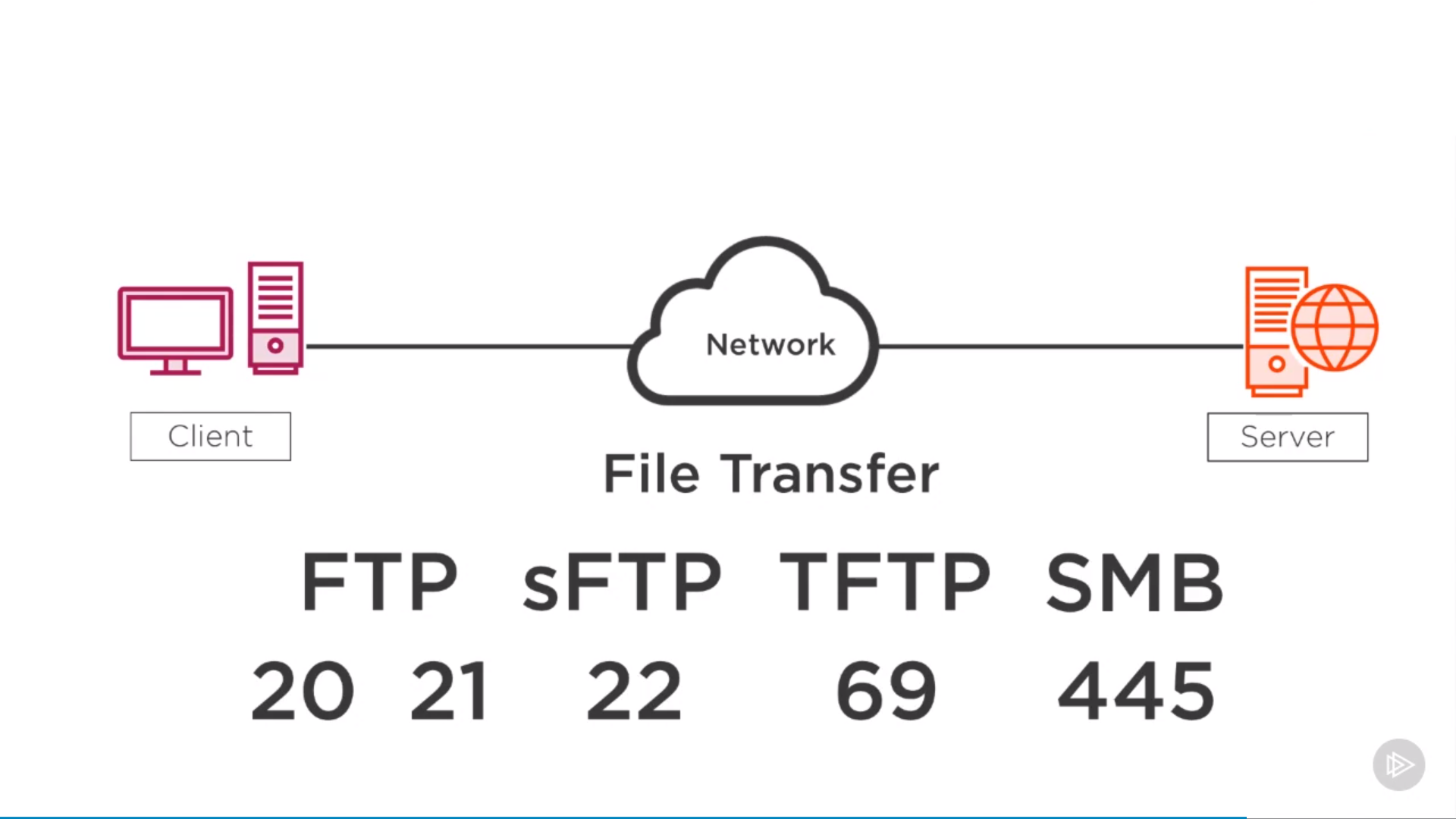
File Transfer
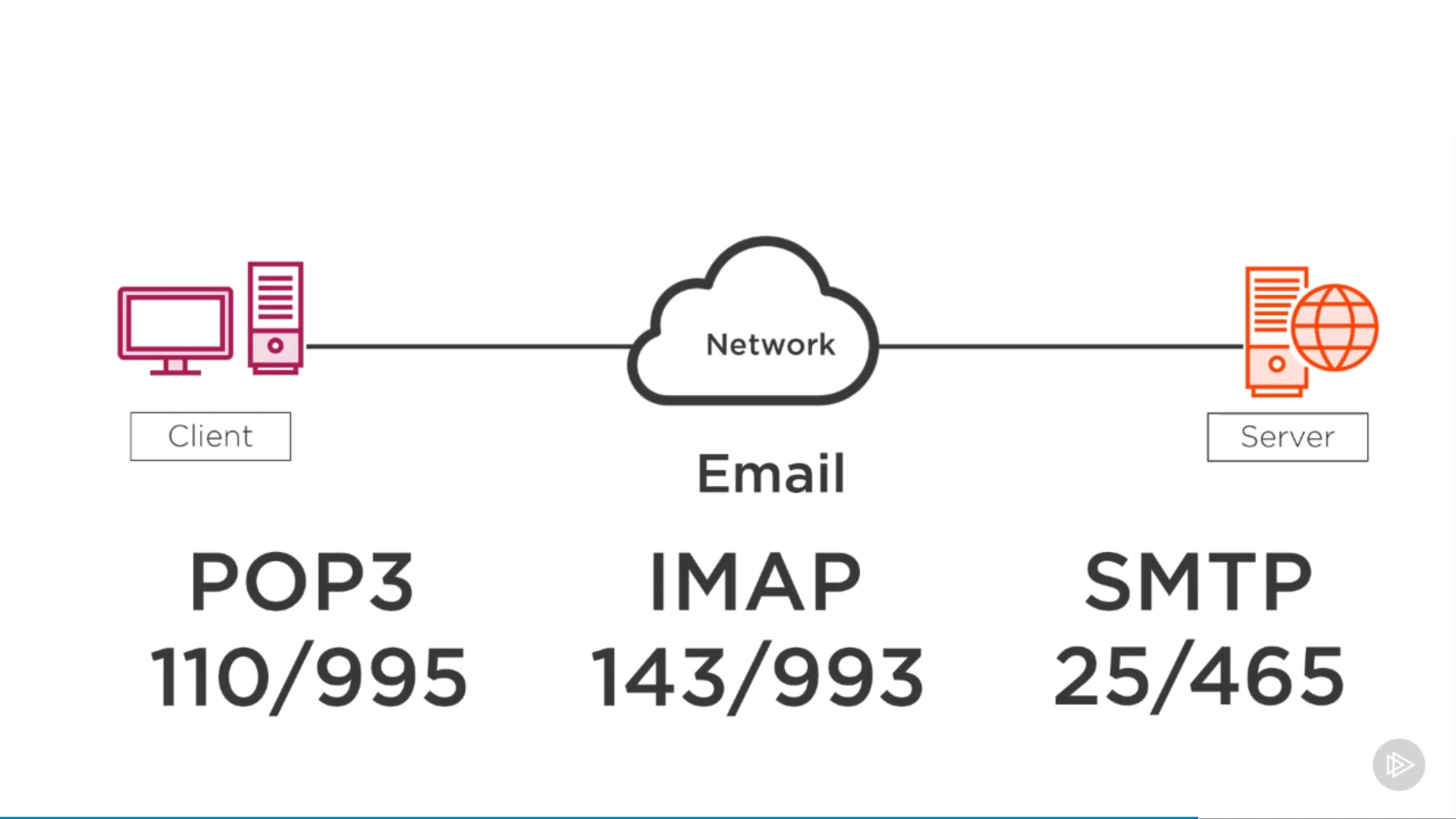
Authentication
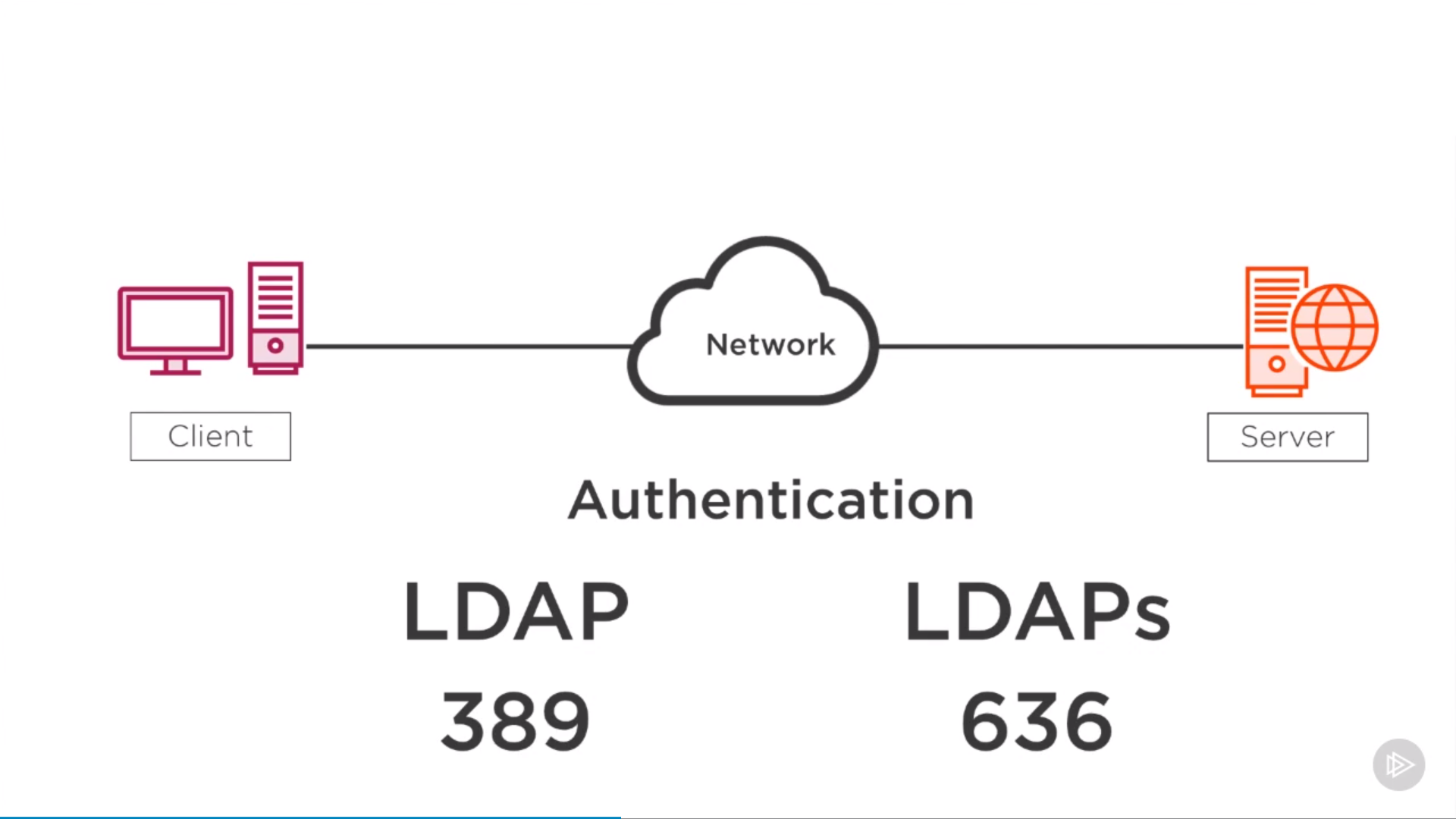
Network Service
Domain Name System(DNS)
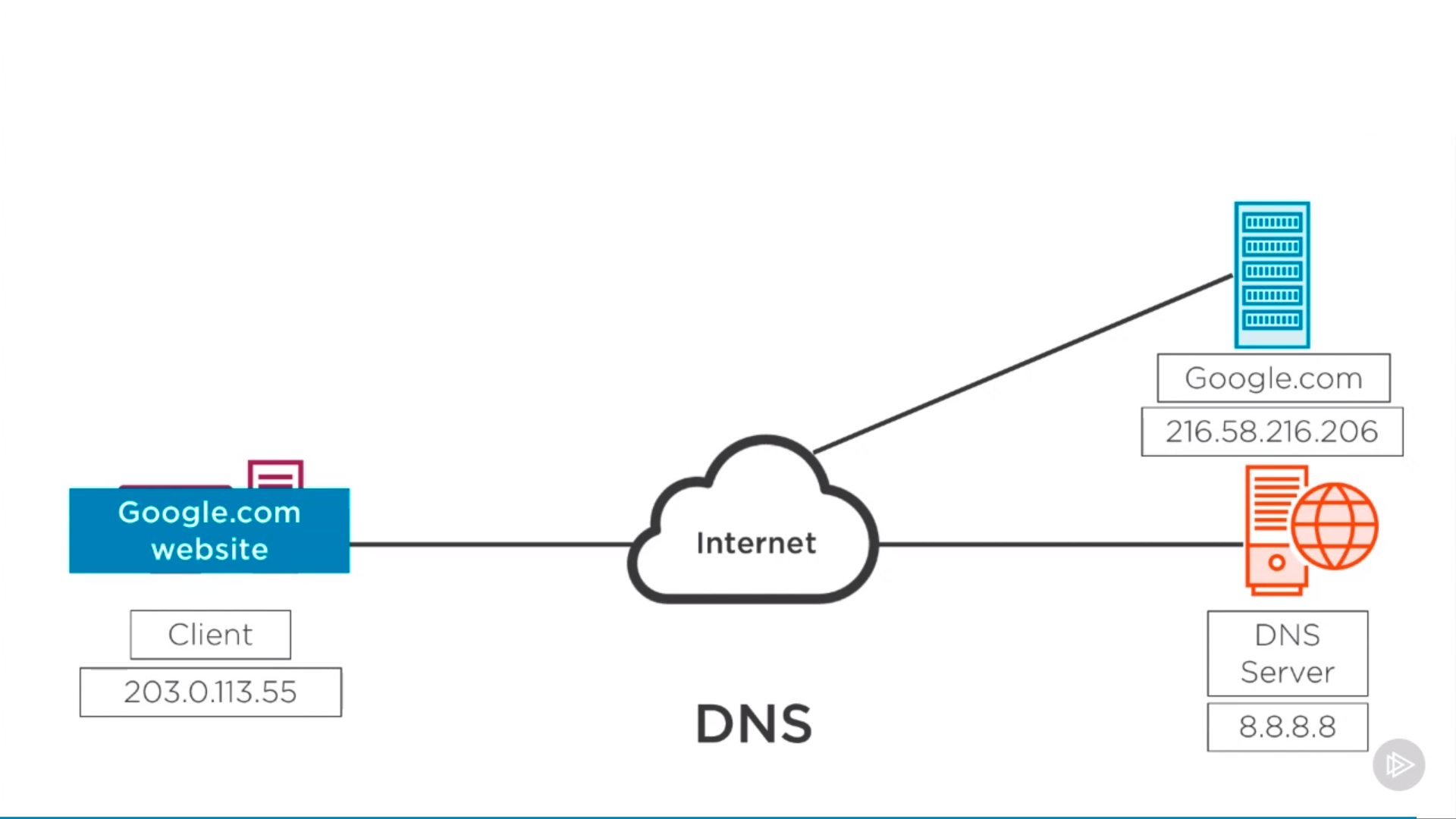
1 | $ nslookup google.com # check google's ip |
1 | $ nslookup |
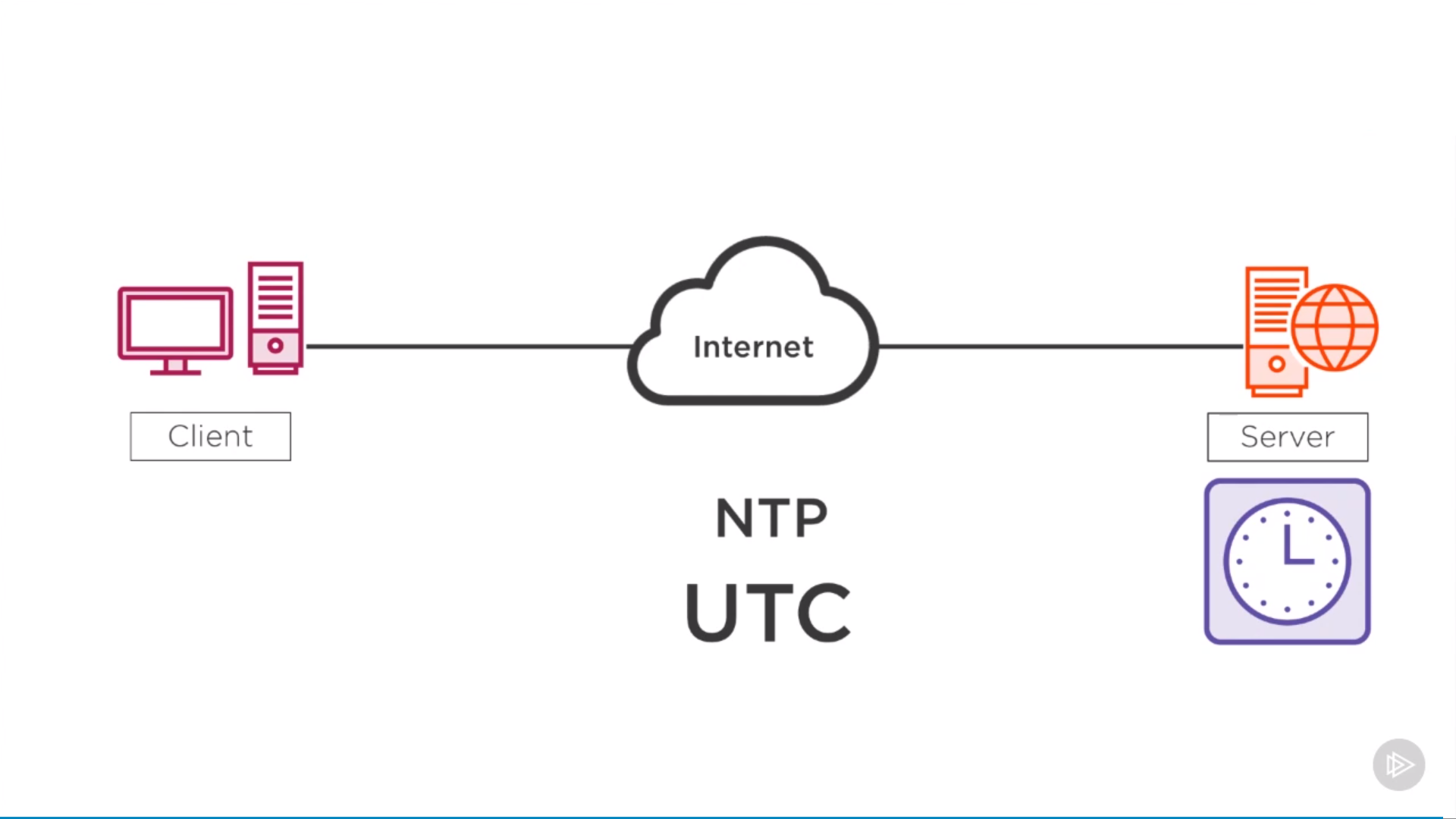
Network Time Protocol(NTP)
Network Management
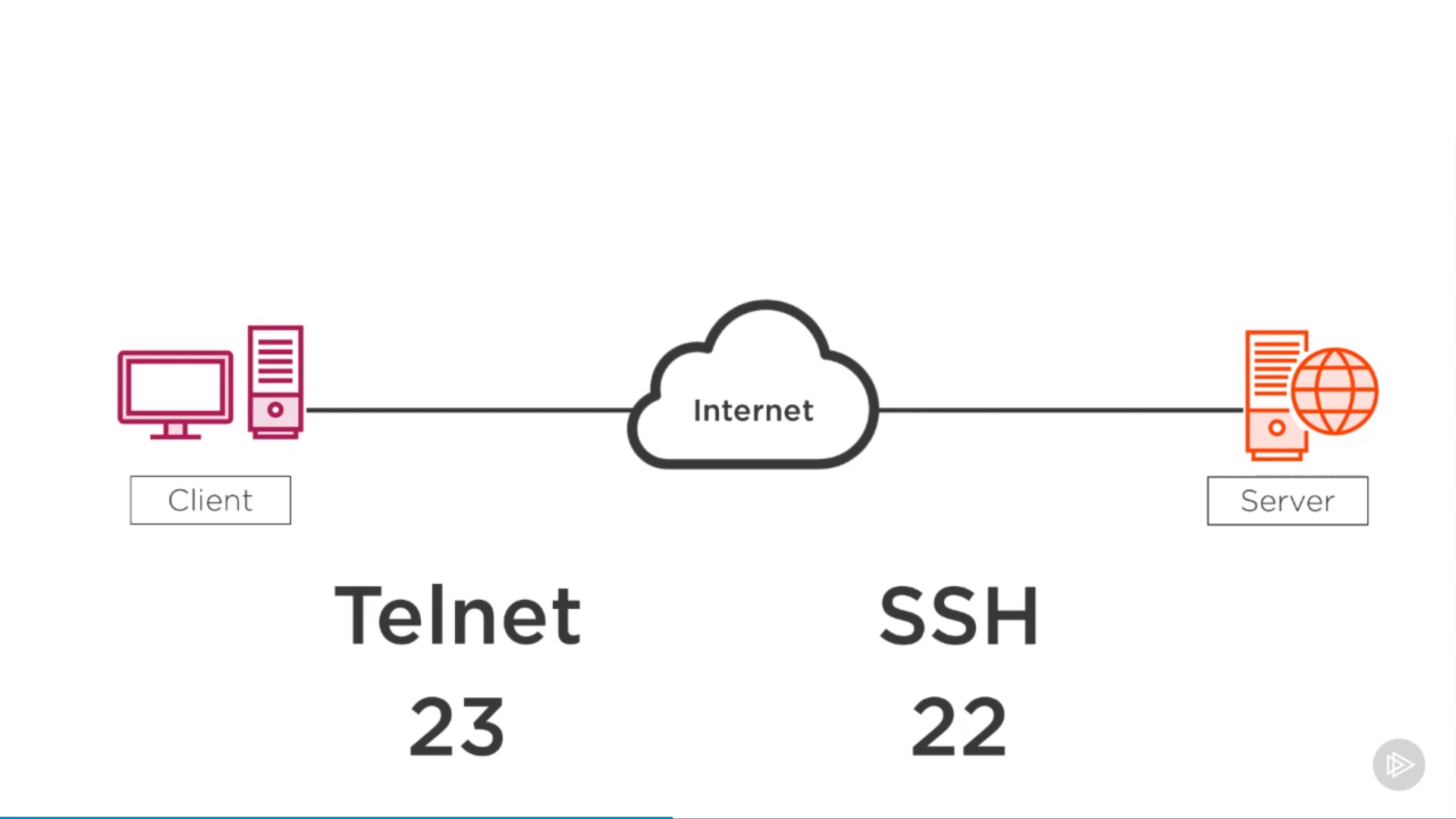
ssh: encryted; telnet: clear text
ssh used encrypt ftp
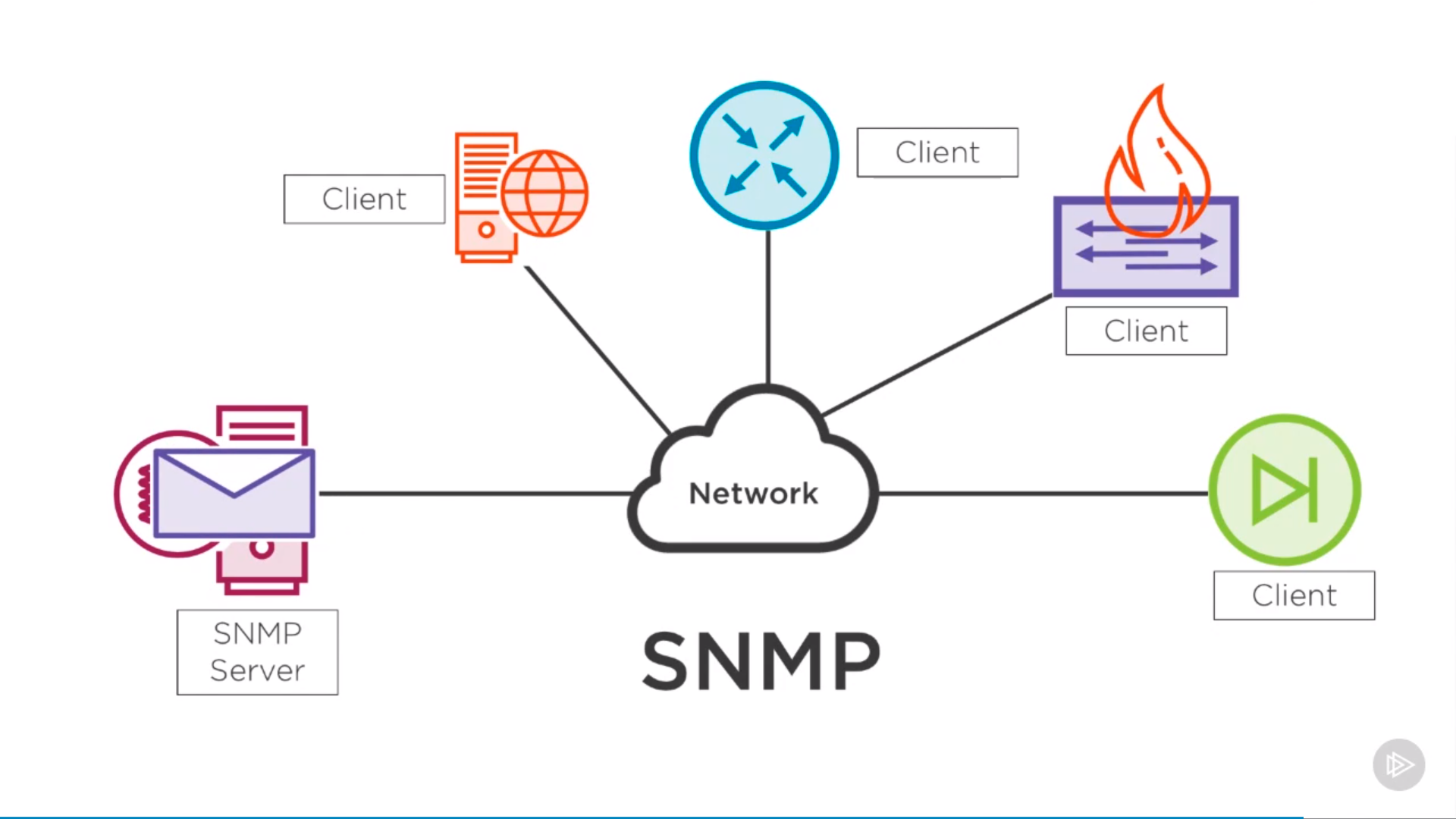
Walk the tree: server collect information(statistics, log) from client
Trap: client send SNMP trap to server
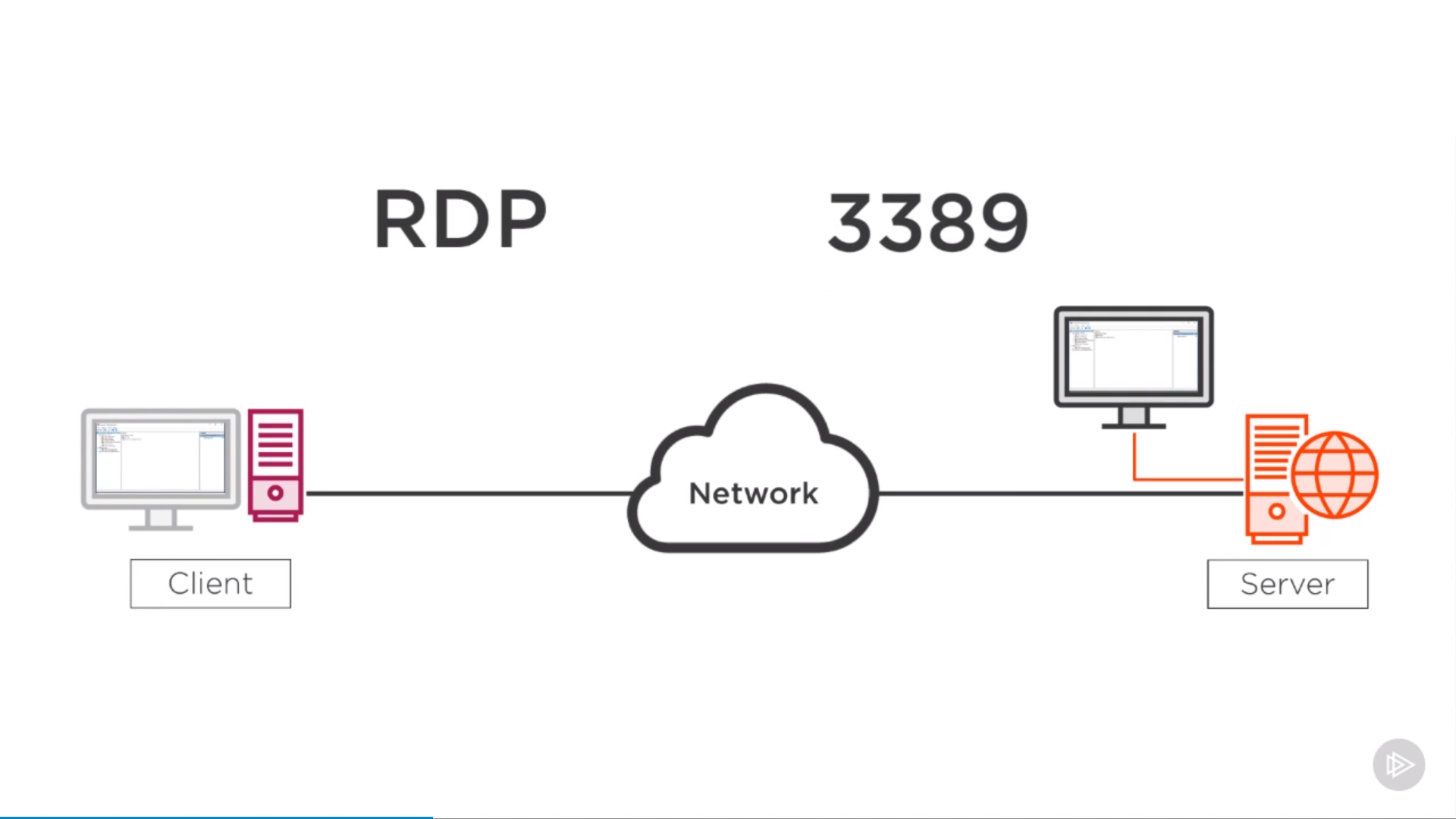
Remote Desktop Protocol(RDP)
Audio/Visual Protocol
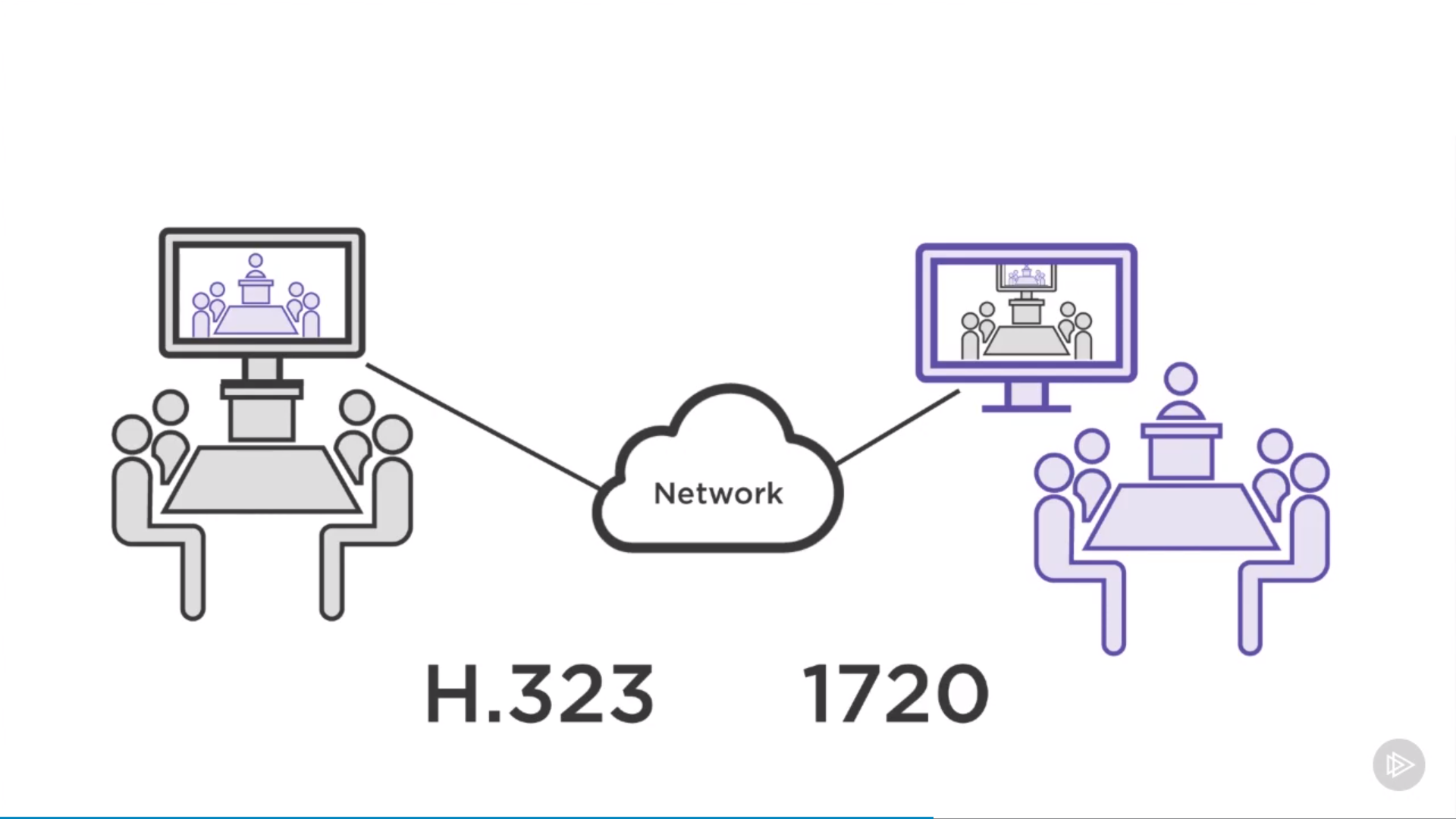
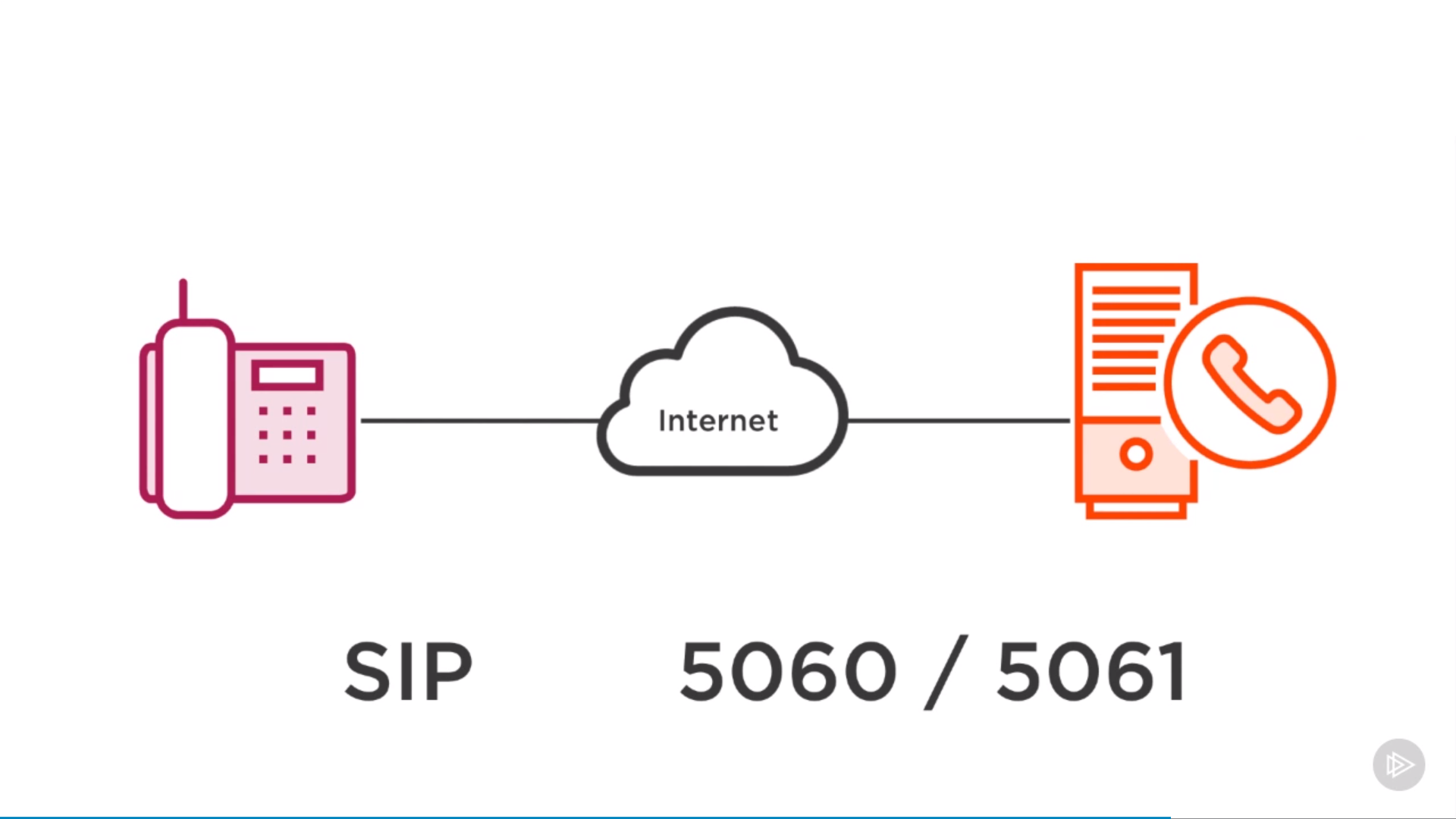
session initiation protocol: voice over ip communication
TCP and UDP
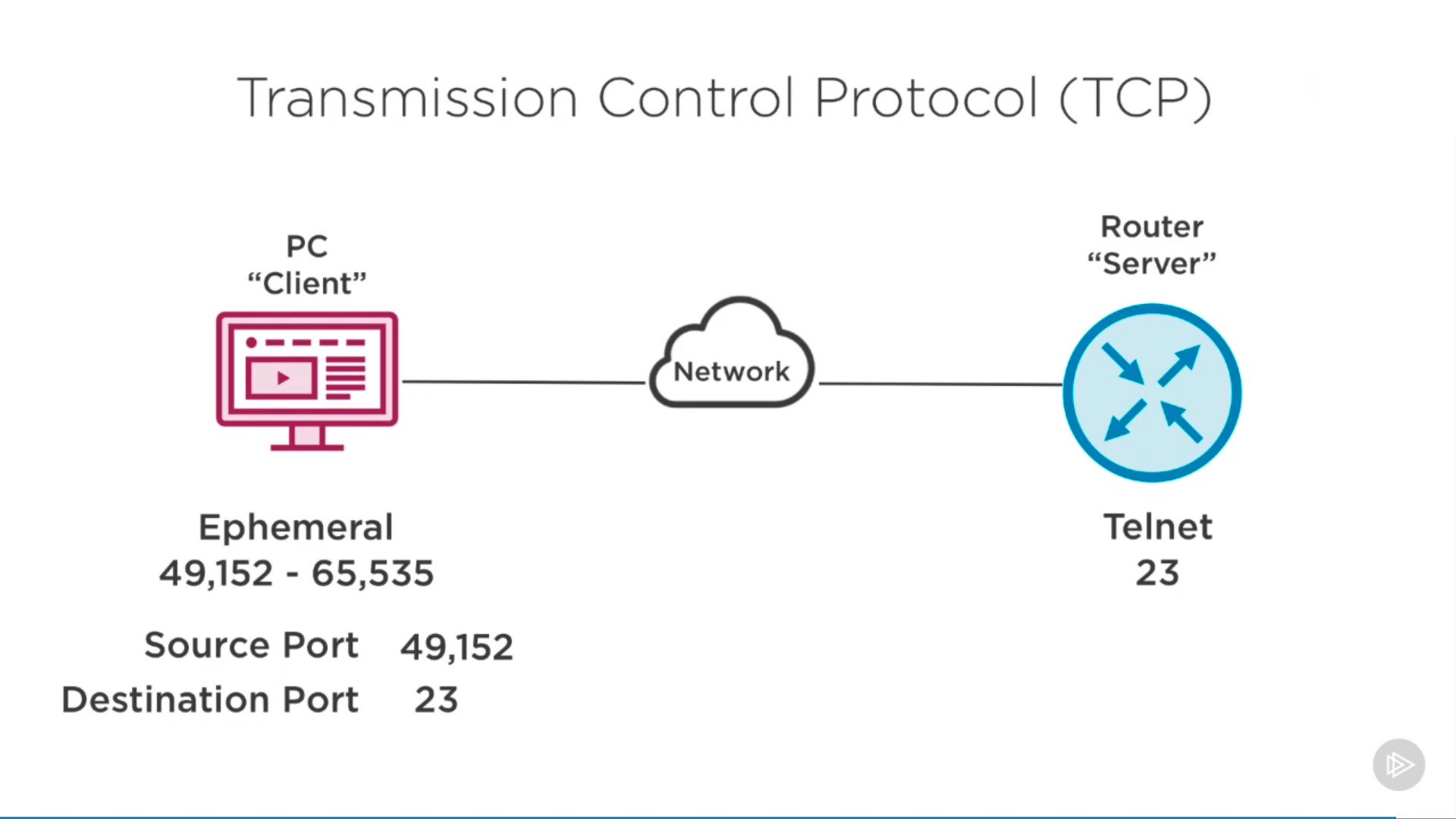
TCP: transmission control protocol
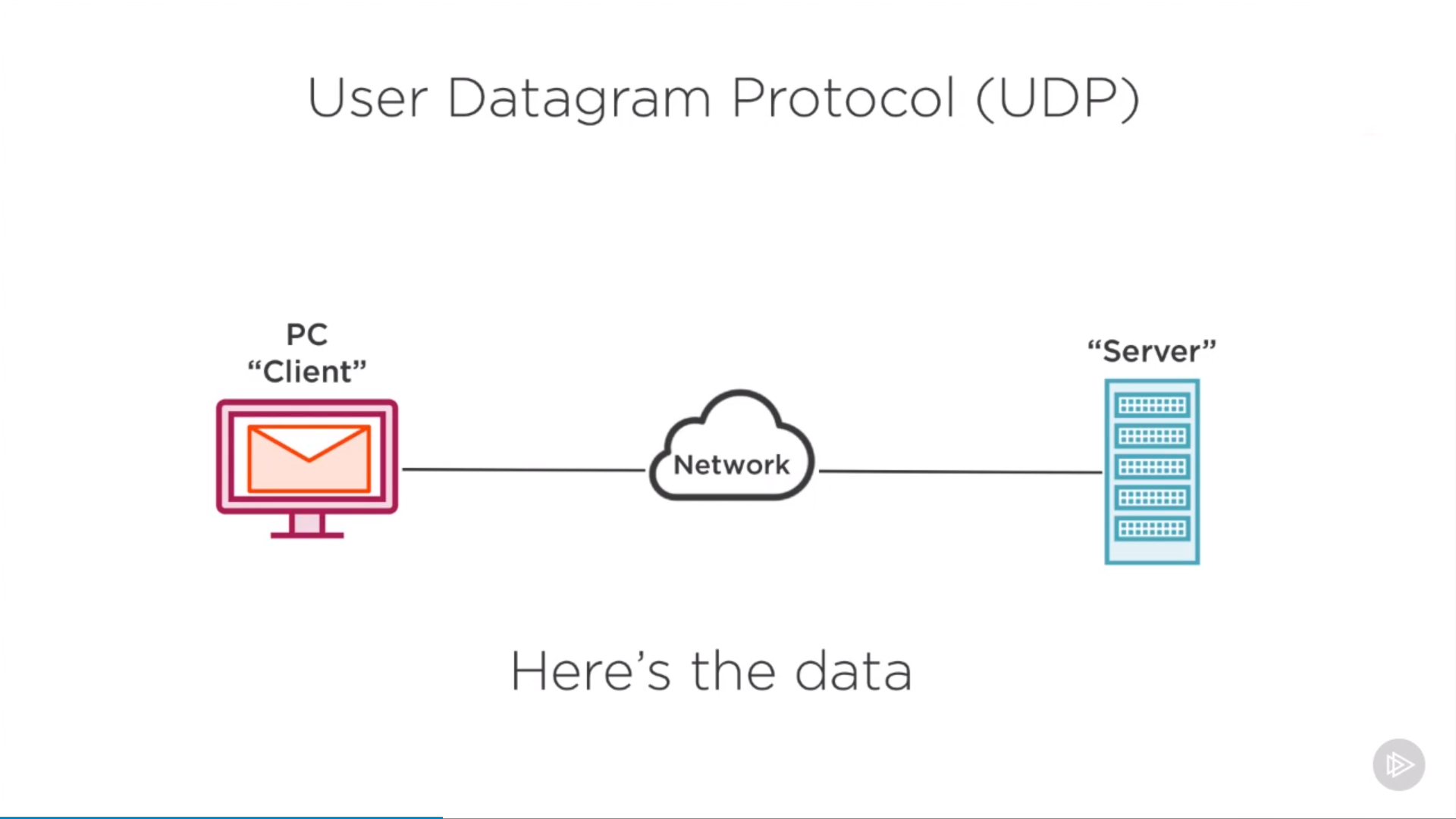
UDP: user datagram protocol
TCP
reliable, verifiable(sequence numbers / acknowledge numbers), notion of session
The 3-way handshake
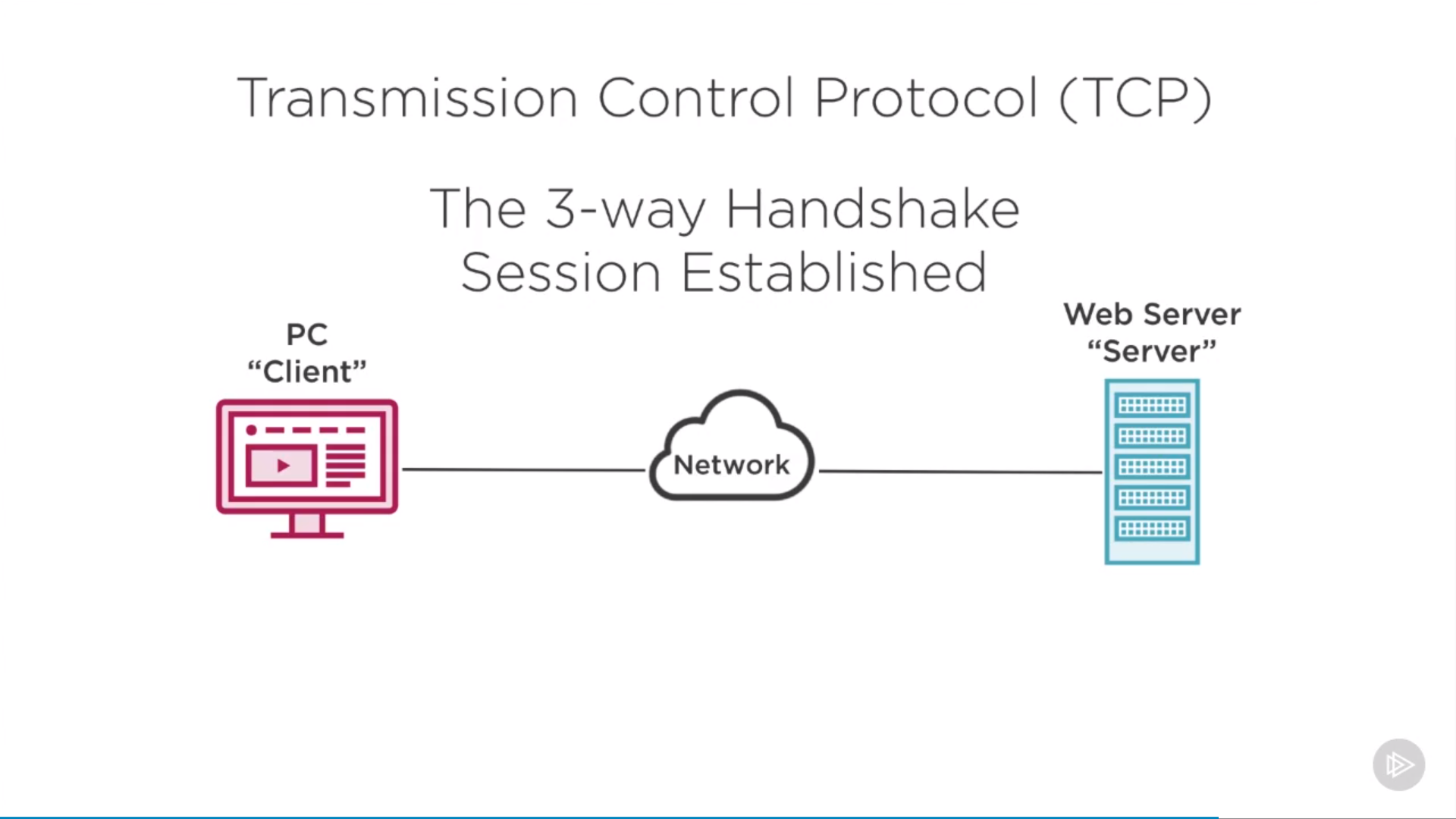
- SYN: send syn msg, wait for reply from server(change state to SYN-RECEIVED)
- SYN-ACK: send msg to client
- ACK: client respond to server
then session establish between client and server by layer 4 protocol
client or server can ask for missing / additional information from each other
then use layer 7 protocol
The 4-way Disconnect
- FIN: server to client
- FIN-ACK: client to server
- FIN: client to server
- FIN-ACK
shutdown the session
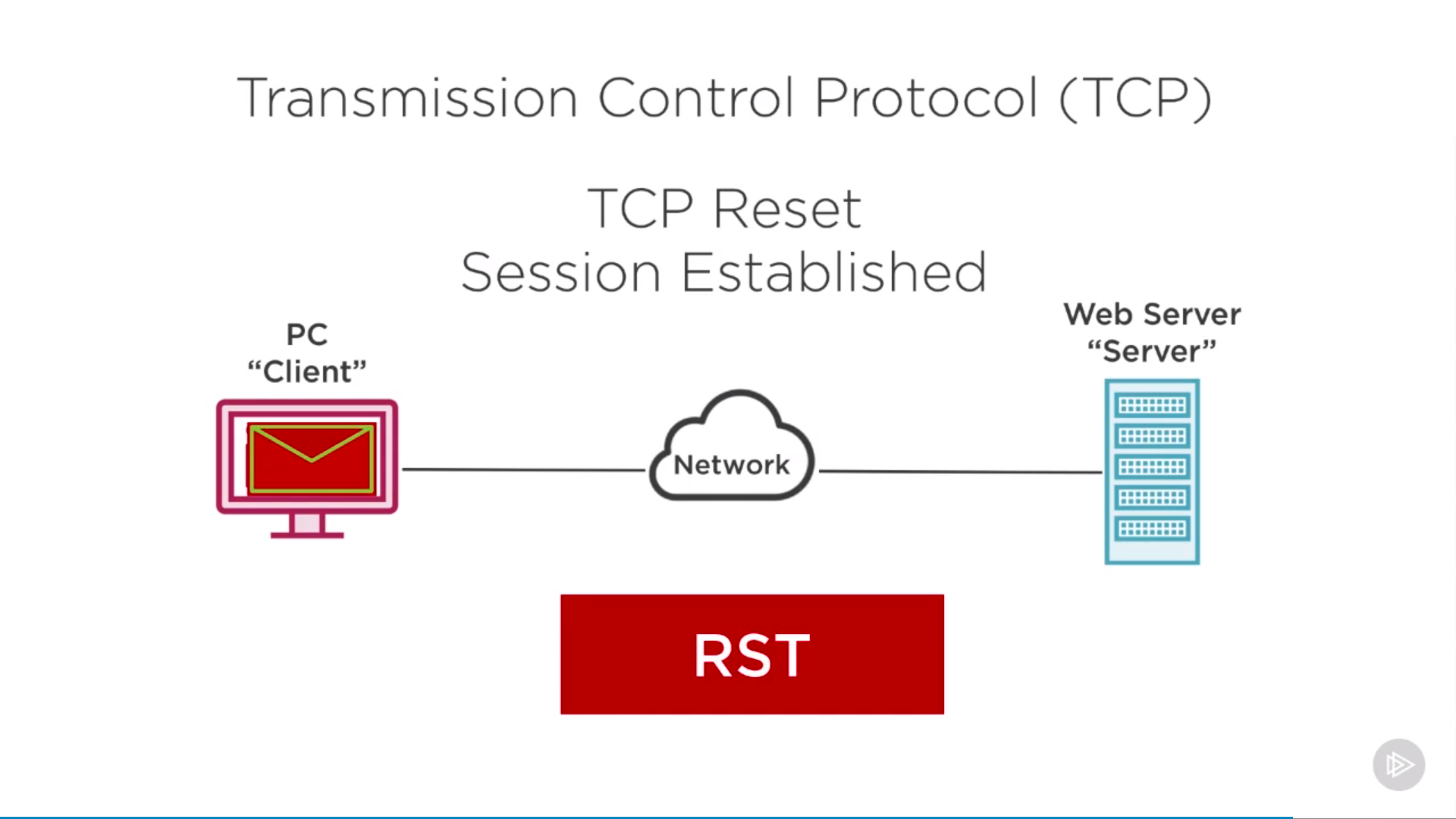
RST: tcp reset, server to client, to shutdown quickly
UDP
no 3-way handshake, no reliable communication, no sequence numbers / acknowledge numbers
very efficient for small data transfer (e.x. DNS)
Port numbers(Transport layer addressing)

Source port and Destination port
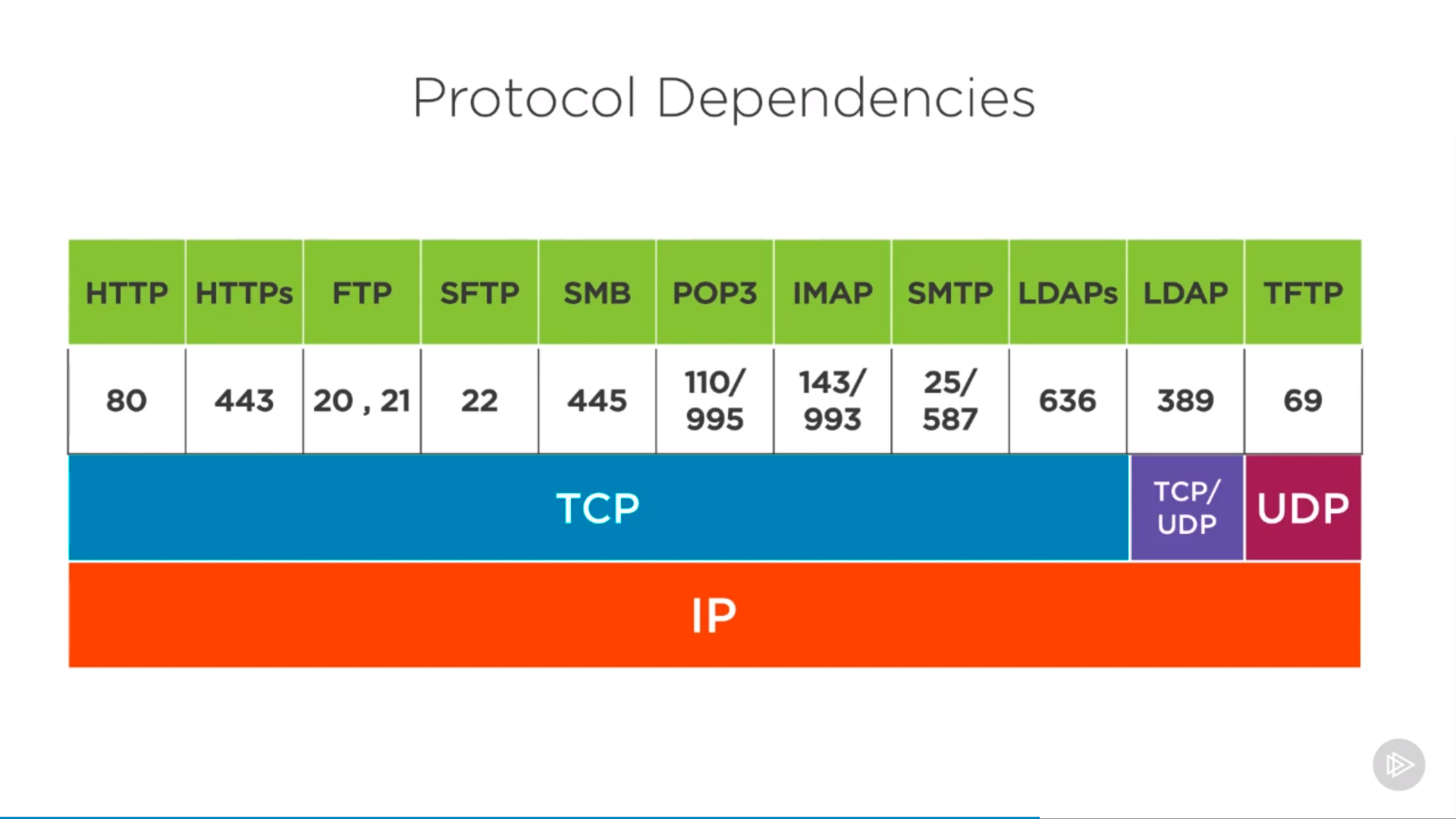
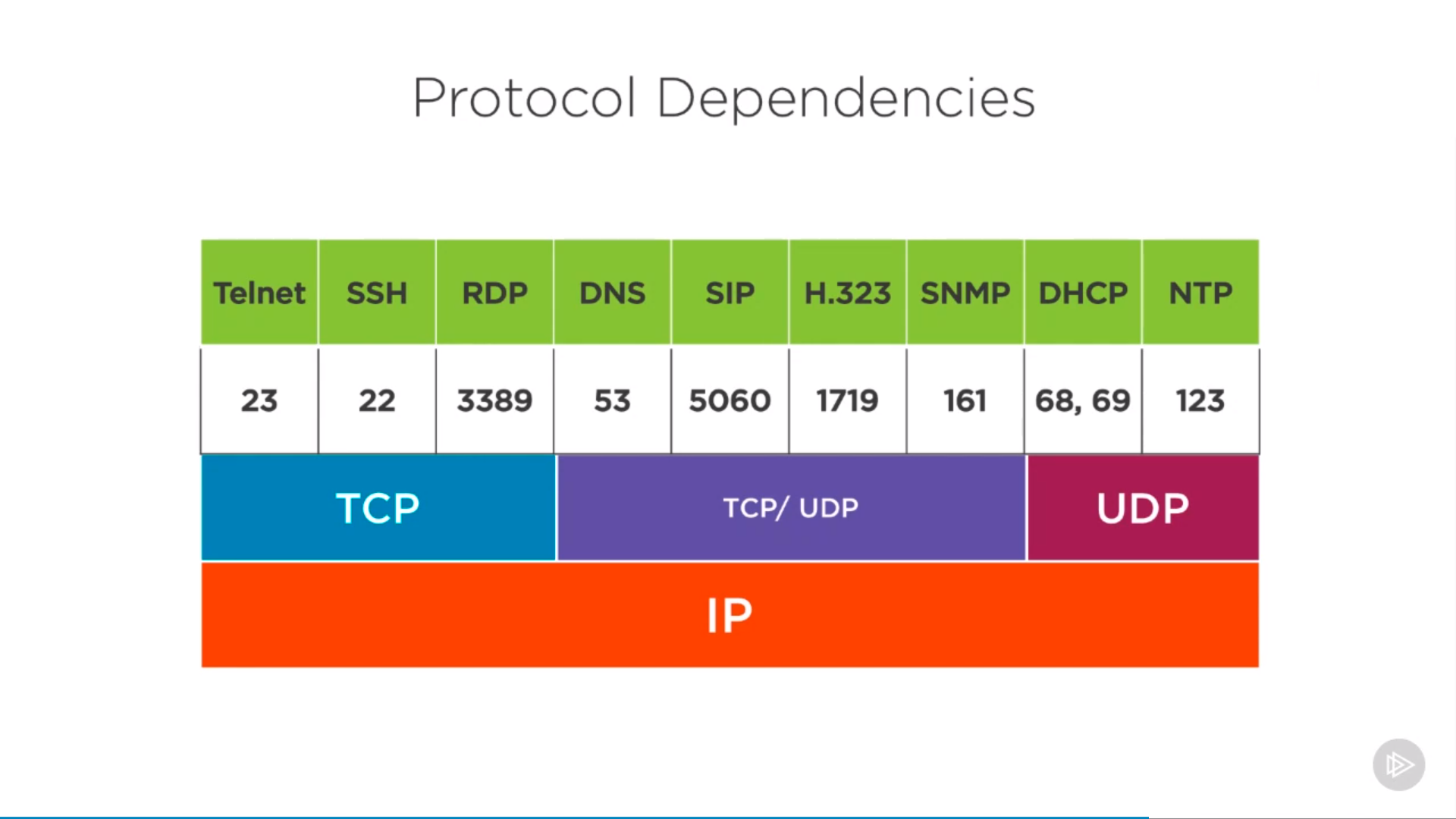
Application layer portocol dependency
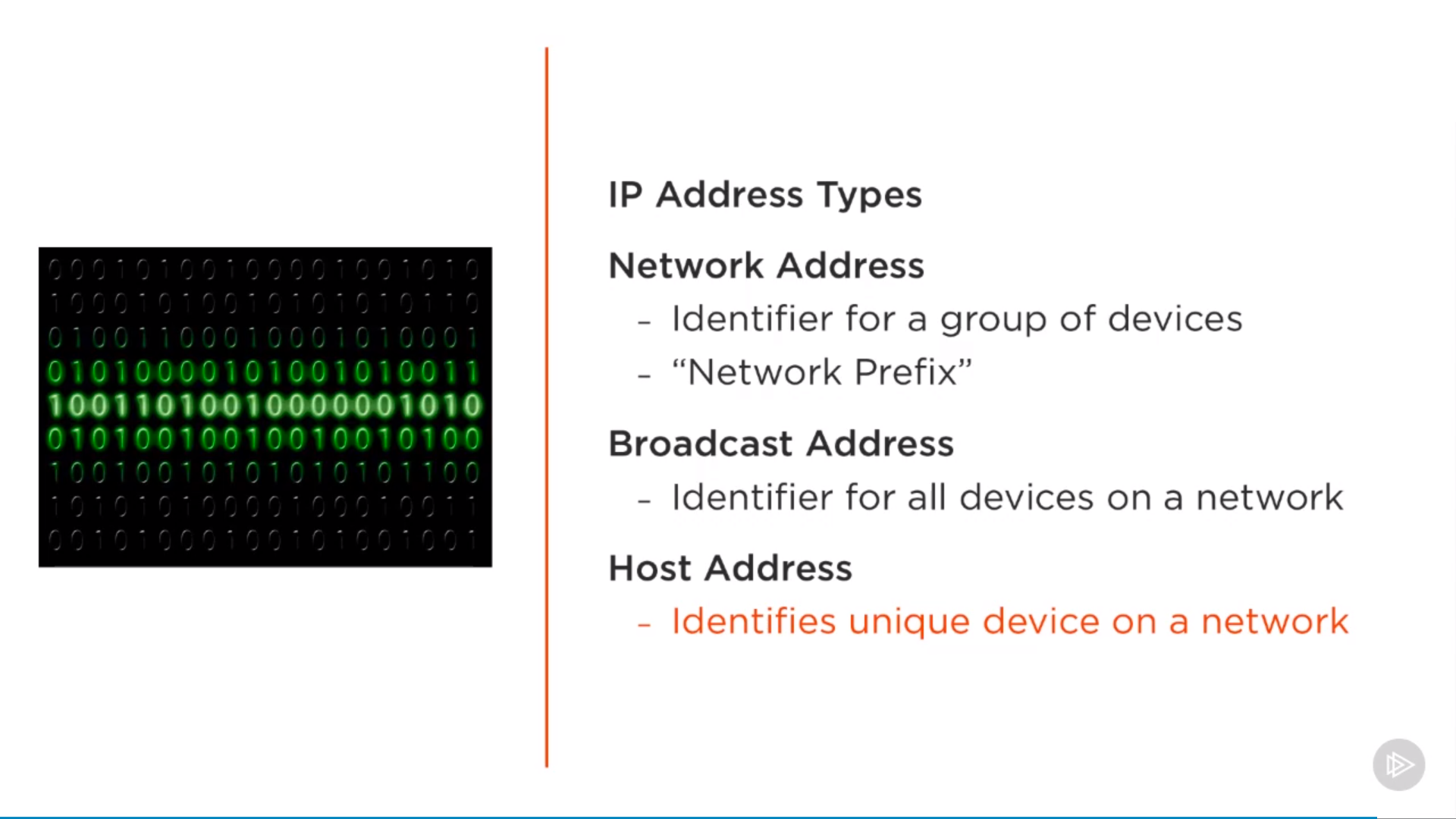
IP Addressing
-
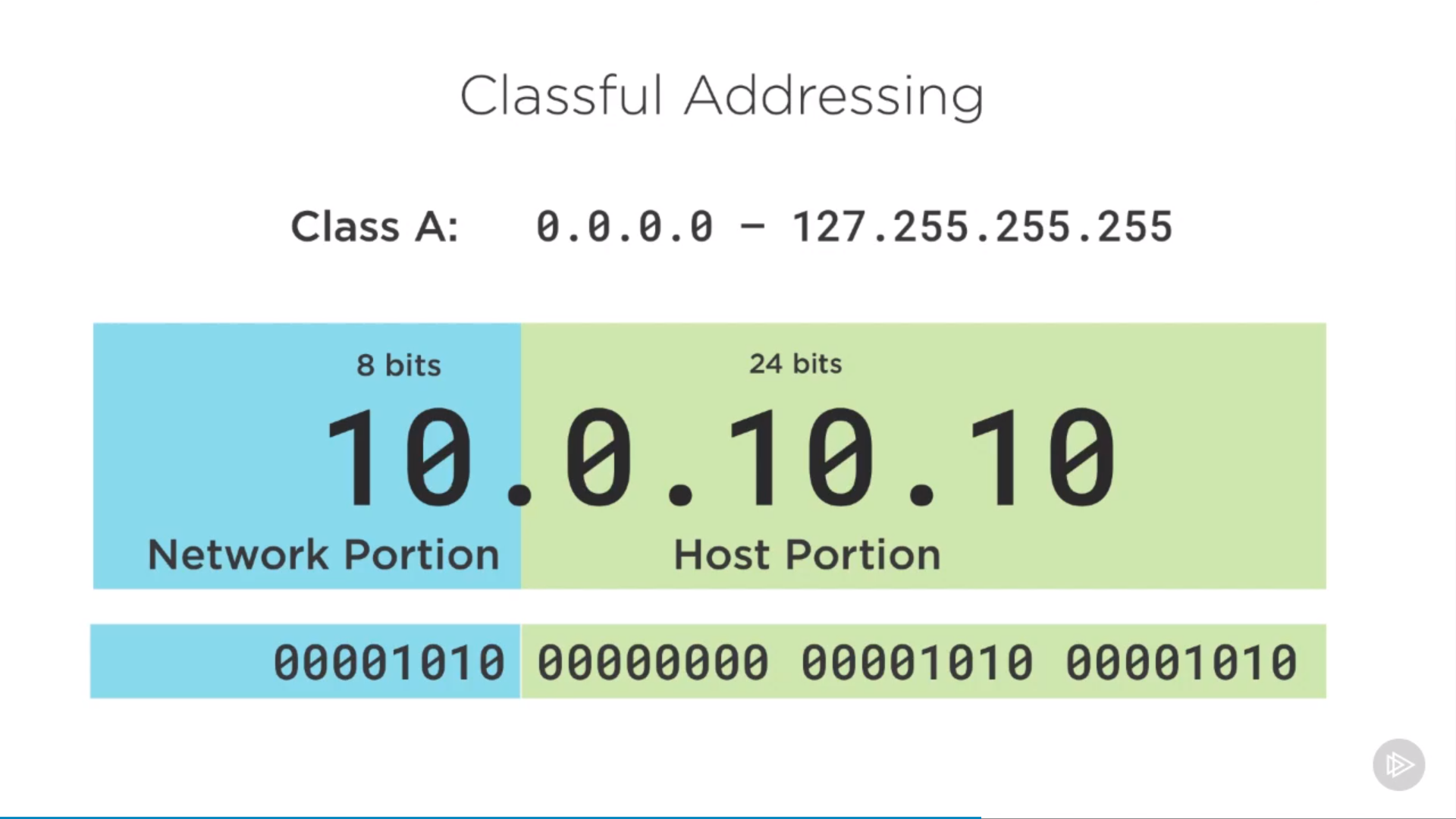
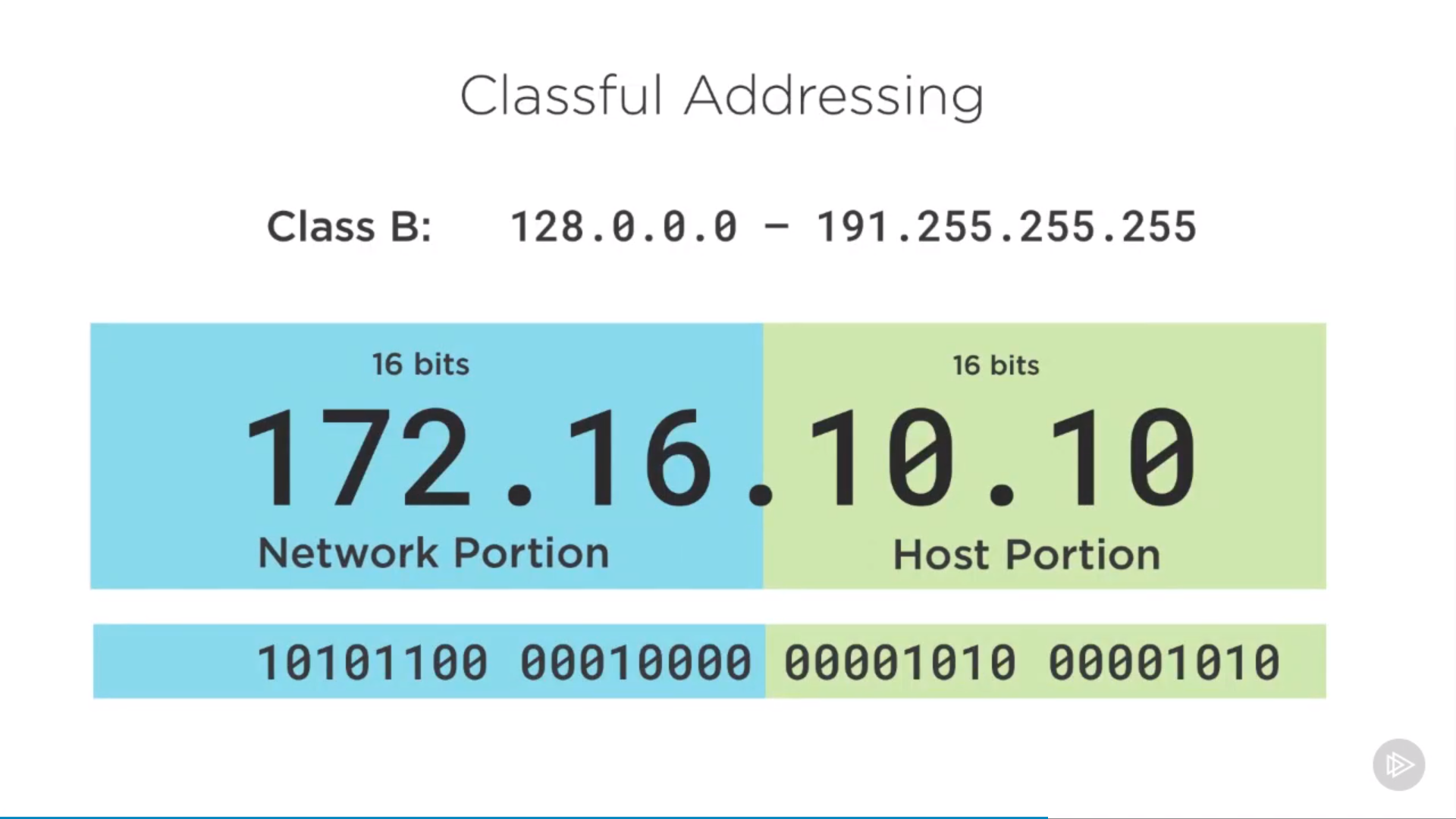
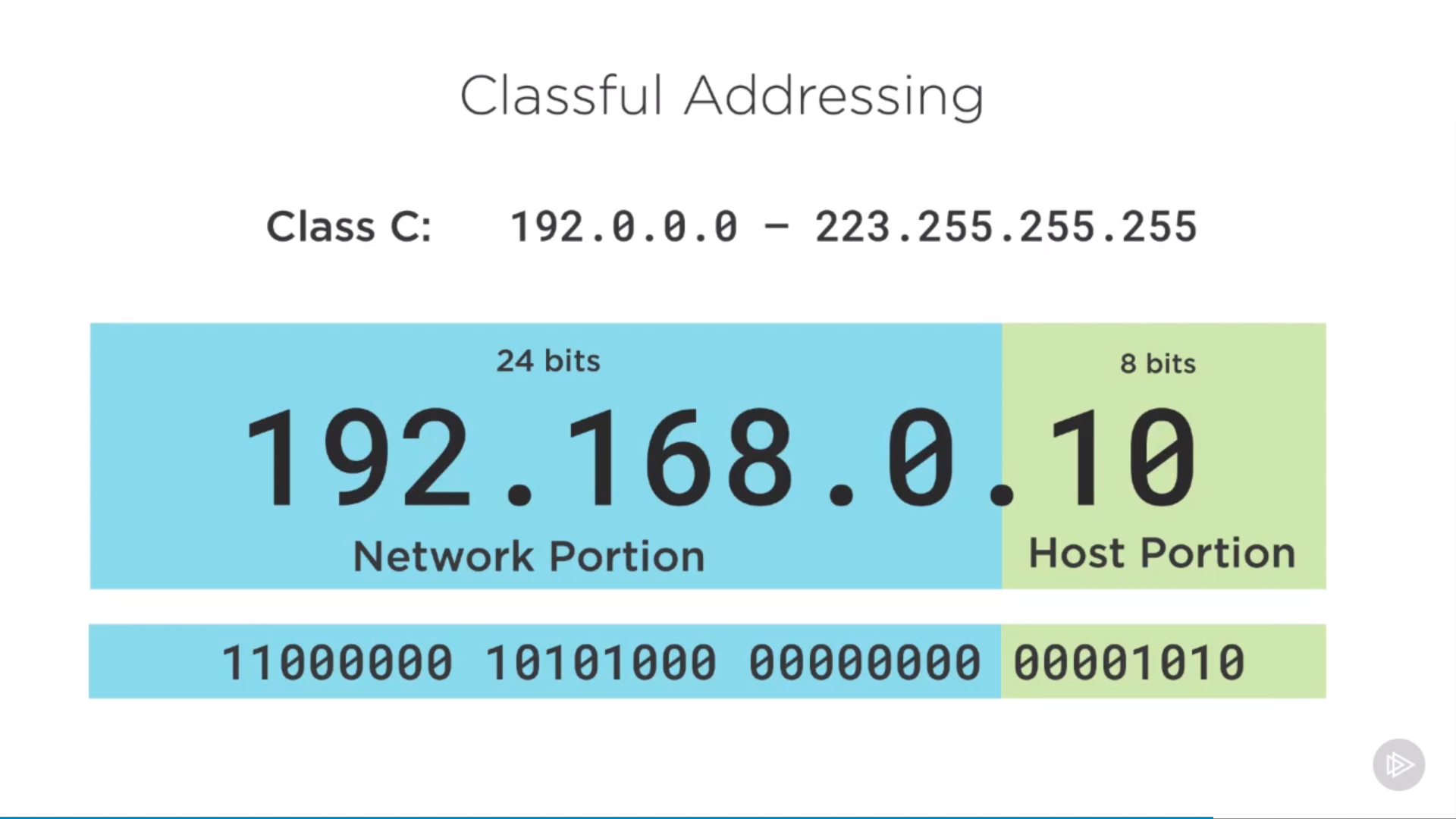
unicast: class A, B, C(public internet), one device to one device
-
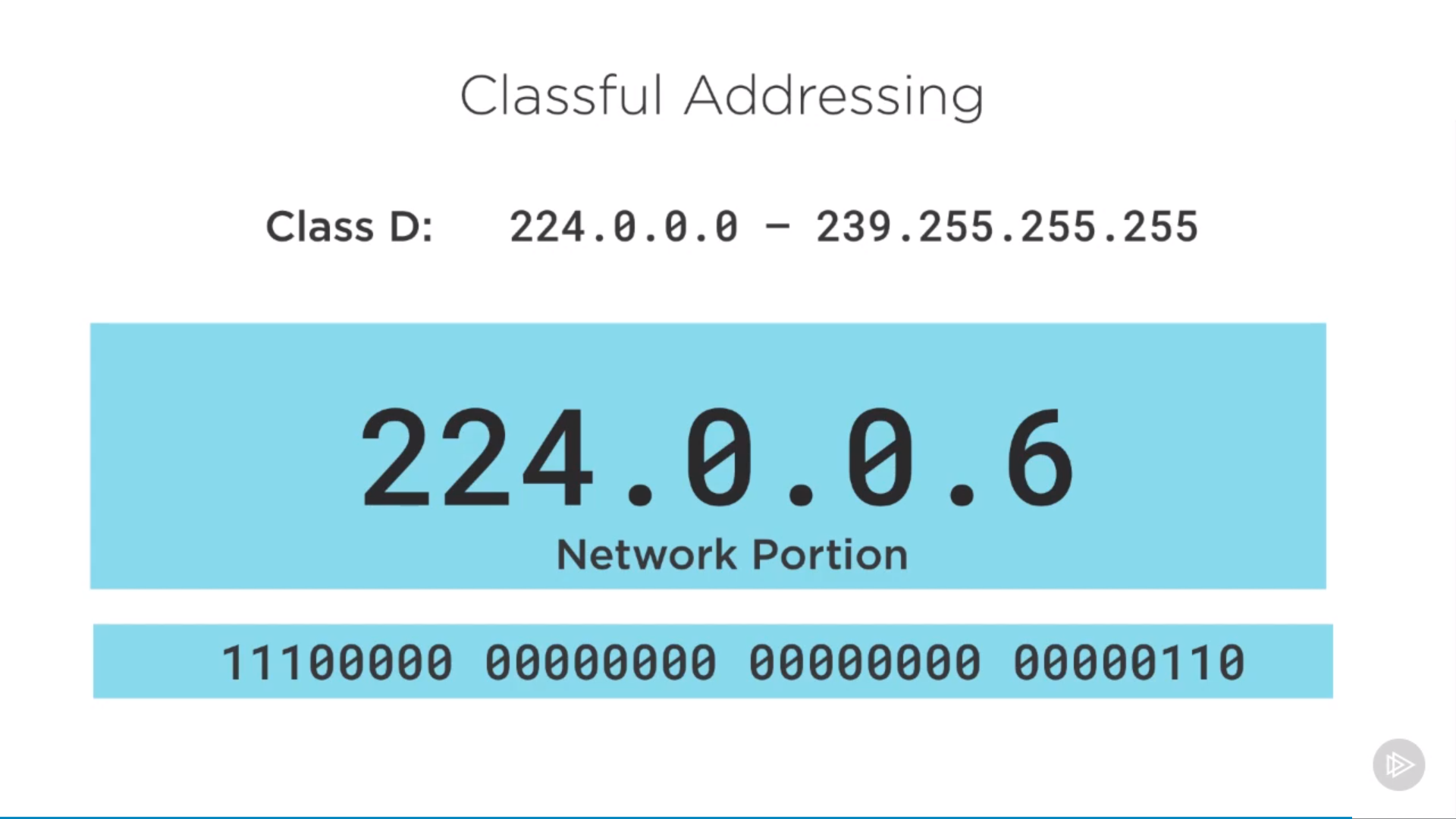
multicast: class D(enterprise org’s live video streamming), one device to many devices
-
experimental: class E
class A
class B
class C
class D
Address types
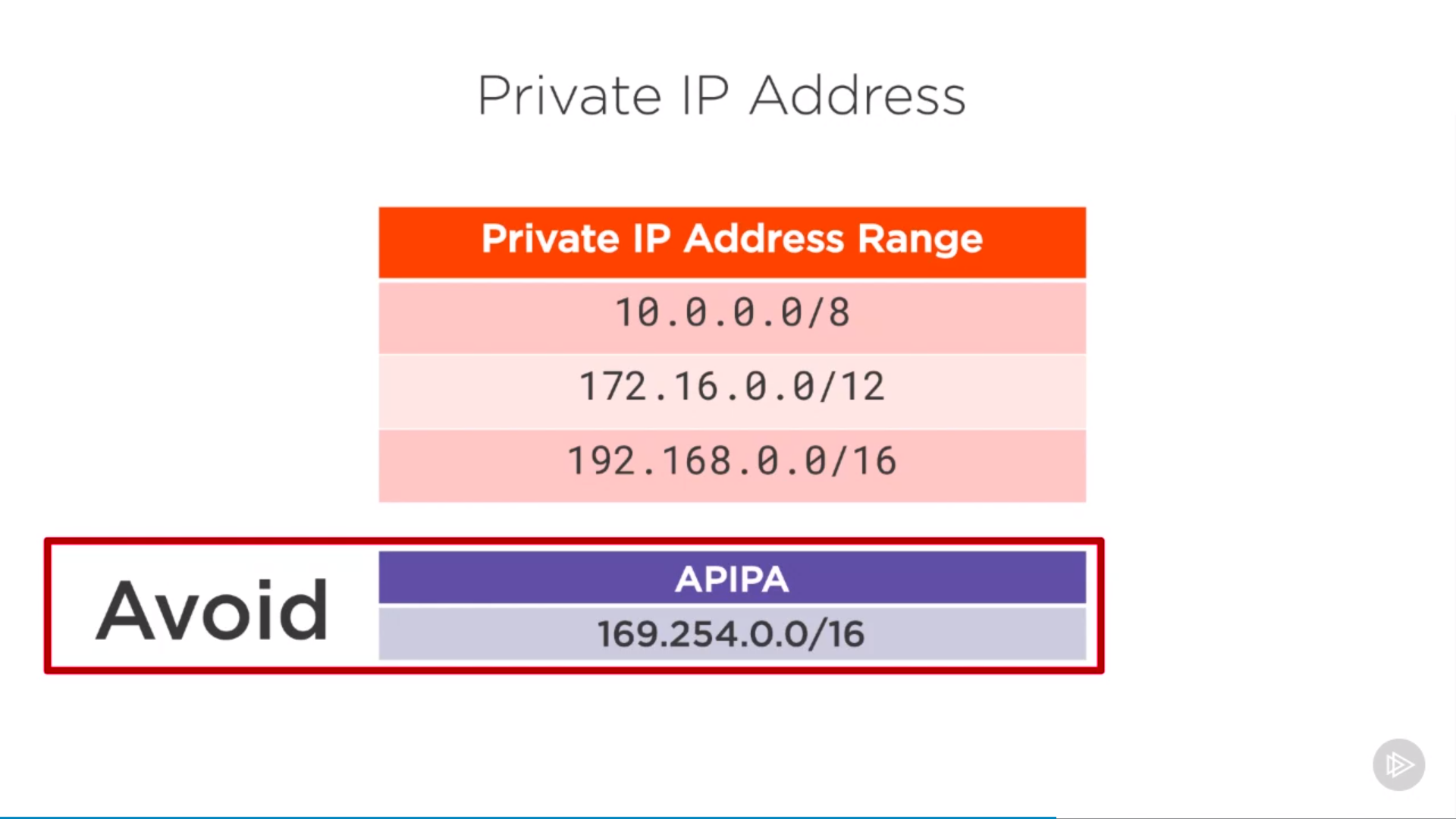
Private ip address
127.0.0.1: loopback address, localhost